Appendix B — Files in Google Colab
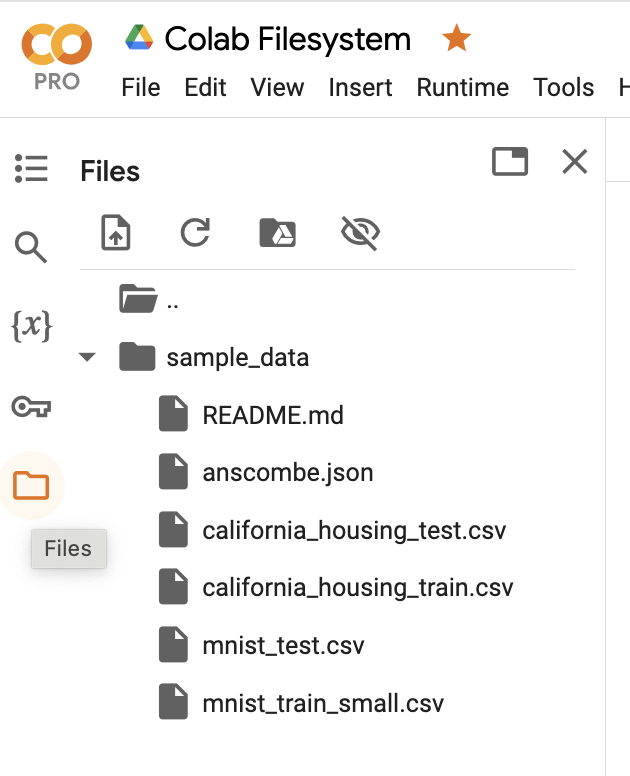
Let’s take a few moments to explore the "Files" menu in the Google Colab left sidebar.
We see there are some example files in the "sample_data" directory:
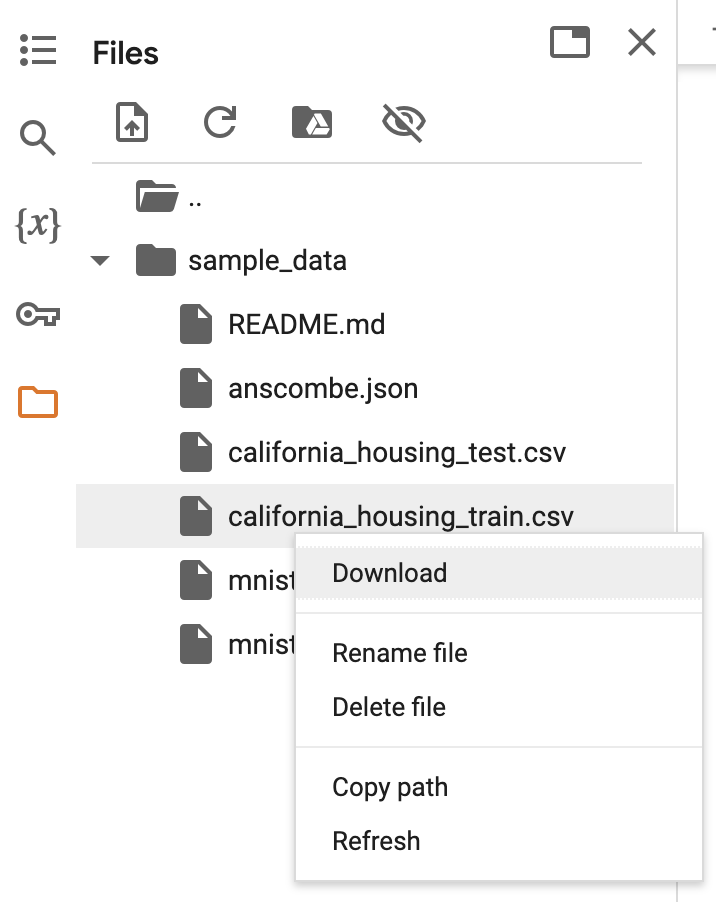
B.1 Downloading Files
Observe, it is possible to download files like these from the Colab filesystem to your local machine, by right-clicking on them:
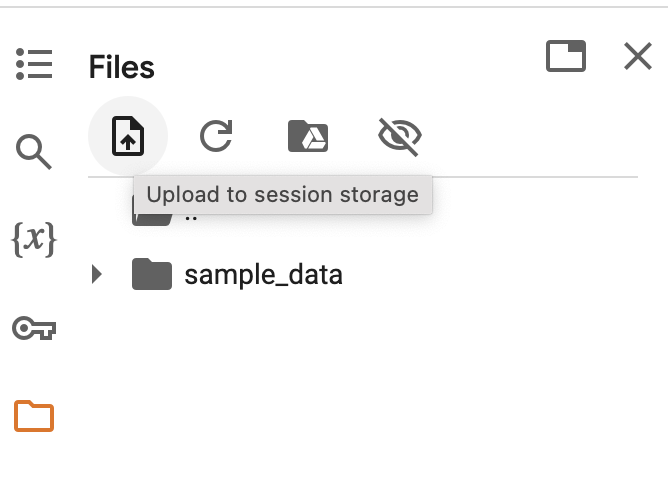
B.2 Uploading Files
And it is possible to upload files from your local machine to the Colab filesystem as well, using the “Files > Upload to session storage” menu option (i.e. the button with the file upload icon):
B.3 Accessing and Manipulating Files
Once we have the files in the Colab filesystem, we can write Python code to access and manipulate them:
One way of interacting with the filesystem in Python is by using the capabilities of the
osmodule.For reading and writing text (".txt") files, we can leverage the
openfunction (see Text File Operations).For reading and writing tabular data (".csv") files, we can leverage the
pandaspackage. Thepandaspackage is a foundational component of the Python ecosystem, and provides capabilities for processing tabular data. Although outside the scope of this book, working with tabular data is covered in more detail in the professor’s Applied Data Science in Python book.
Some of these examples might seem a bit complicated at the moment for beginners. For now, the main take-away is understanding there are ways for us to write Python code to interact with the surrounding environment, specifically accessing and manipulating the filesystem.